Hands-on : Local alignment and HIV drug resistance#
Background#
HIV lifecycle#
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system. The figure below shows the life cycle of HIV.
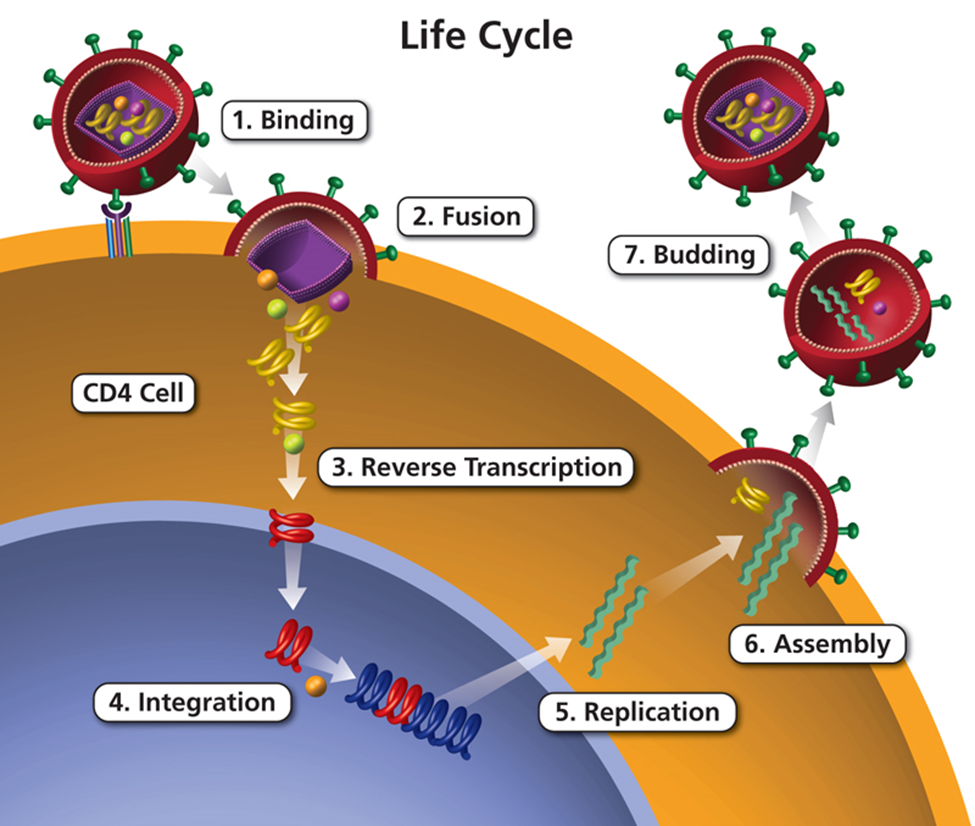
Fig. 31 Lifecycle of HIV
Source:https://hivinfo.nih.gov/understanding-hiv/fact-sheets/hiv-life-cycle#
Note that reverse transcription is a key part of the life cycle. Reverse transcription is carried out by an enzyme called reverse transcriptase, which is encoded in the HIV genome (segment labeled RT in the the pol region in the figure below of the structure of an HIV genome).
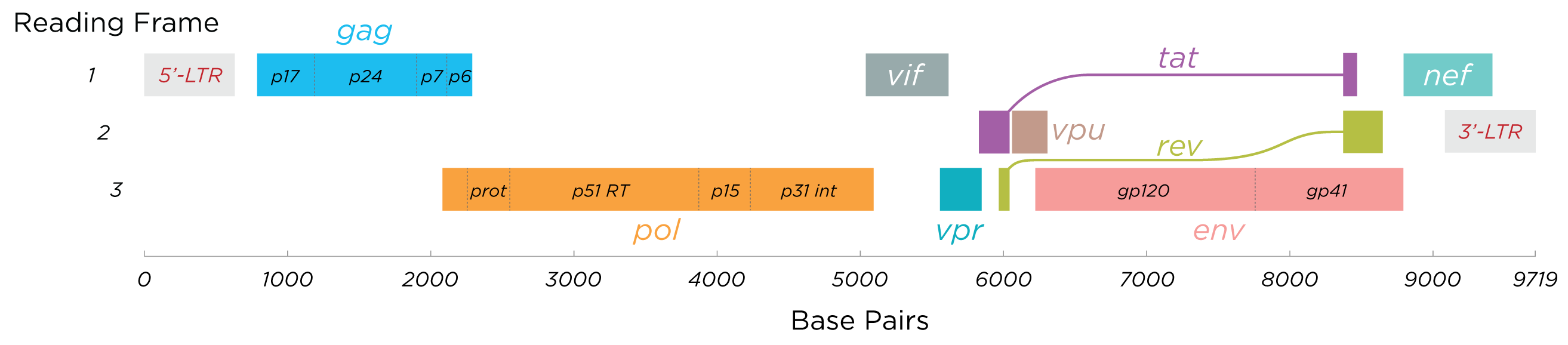
Fig. 32 Genome of HIV
Source:https://hivinfo.nih.gov/understanding-hiv/fact-sheets/hiv-life-cycle#
Mutations and drug resistance#
Mutations in the RT gene can lead to altered reverse transcriptase enzymes, which are no longer affected by the drugs. Here is a catalog of drug resistant mutations including those conferring resistance to NRTIs. Here is another one.
What is worrisome is that we are seeing increasing drug resistance levels even in ART-naive patients, that is those have not initiated ART.
High-throughput sequencers for HIV surveillance#
In recent years, high-throughput sequencers have been replacing the older Sanger sequencing technology in sequencing HIV genomes from patients to monitor drug resistance mutations. The newer sequencers can read a lot of sequences enabling discovery of variants that are present in low abundances.
Here is one study that uses modern sequencers to survey the levels of HIV drug resistance in ART-naive individuals. The sequence data they produced is available here.
Objective#
Identify and estimate the prevalence of HIV drug resistance mutations in an ART-naive individual by aligning sequence reads of HIV genome obtained from a patient to the reference HIV genome HXB2.
Method#
Get HIV sequence data from 1 patient from the study above. This will be in fastq format.
Obtain the HXB2 reference sequence and annotation from here.
You will be using LAST for the local alignment of reads to the reference.
Compute a suffix array of the reference using
lastdb.Train the scoring scheme using
last-train.Perform local alignment of reads to the reference using
lastal.Write a script to go through the sites of interest relevant to NRTI resistance (to make things simpler, you can just choose one drug e.g. zidovudine), and report on the mutations you can identify.
References#
John Herron, Scott Freeman, Chapter 1: A Case for Evolutionary Thinking: Understanding HIV, Evolutionary Analysis, Fifth Edition (2015), Pearson.
https://www.iasusa.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/33-2-mutations.pdf
https://hivdb.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/PositionPhenoSummary.cgi
